Off grid living solar generator systems are transforming how people power their homes in remote locations. This technology offers a compelling alternative to traditional grid electricity, providing independence and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. But the transition to off-grid living requires careful planning, encompassing system design, energy management, and financial considerations. This article explores the intricacies of off-grid living powered by solar, from initial setup to long-term sustainability.
Choosing off-grid living involves a significant lifestyle shift, demanding careful consideration of location, resource availability, and the specific energy demands of your chosen lifestyle. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of solar generator technology is paramount. This includes selecting the appropriate solar panels, battery storage, and inverter to meet your needs, while also implementing energy-saving practices to optimize efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
The financial aspects, including initial investment, maintenance costs, and potential long-term savings, are equally crucial factors in making an informed decision.
Understanding Off-Grid Living: Off Grid Living Solar Generator
Off-grid living represents a deliberate departure from the conventional reliance on centralized utilities and services. Individuals and families choosing this lifestyle prioritize self-sufficiency and a reduced environmental footprint, often embracing a simpler way of life. This decision involves careful planning and a significant commitment to resource management.Off-grid living encompasses a broad spectrum of choices, from completely self-sufficient homesteads to partially off-grid setups relying on some grid connections for specific services.
The degree of self-reliance varies greatly depending on individual circumstances and resources.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Off-Grid Living
The appeal of off-grid living lies in its potential for greater independence and connection with nature. Individuals often cite freedom from utility bills, reduced environmental impact, and a slower pace of life as key advantages. However, this lifestyle also presents challenges. Self-sufficiency demands significant time, effort, and often substantial upfront investment in infrastructure such as solar panels, water collection systems, and backup power solutions.
Furthermore, remote locations can present difficulties in accessing healthcare, education, and social connections.
Essential Considerations for Choosing an Off-Grid Location, Off grid living solar generator
Selecting an appropriate location is paramount for successful off-grid living. Factors to consider include access to water sources (wells, springs, rainwater collection), suitable land for building and cultivating food, sunlight exposure for solar energy generation, and proximity to essential services (even if limited). Legal aspects, such as land ownership and building permits (where applicable), must also be carefully navigated.
The availability of internet connectivity, while not strictly essential, can significantly improve communication and access to information in remote areas. Local climate conditions, including temperature extremes, precipitation patterns, and potential natural hazards, will directly impact infrastructure design and resource management.
Comparison of Off-Grid Living Setups
The initial cost and ongoing maintenance of an off-grid system can vary greatly depending on the chosen setup and level of self-sufficiency desired. Below is a comparison of some common options:
| Setup Type | Pros | Cons | Initial Cost (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimalist Cabin with Solar Power | Low initial investment, relatively simple to maintain. | Limited living space, dependence on solar power (intermittent), potential for limited comfort. | $20,000 – $50,000 |
| Self-Sufficient Homestead with Extensive Infrastructure | High degree of self-sufficiency, potential for food production, greater comfort. | High initial investment, significant ongoing maintenance, requires extensive knowledge and skills. | $100,000 – $500,000+ |
| Tiny Home with Off-Grid Capabilities | Portability, lower initial cost compared to larger homes, reduced environmental impact. | Limited living space, potential for challenges with off-grid systems in different locations. | $30,000 – $80,000 |
| Converted RV or Van with Solar Power | Mobility, relatively low initial cost, adaptable to various locations. | Limited living space, potential for reliance on campsites or boondocking areas, limited storage. | $15,000 – $40,000 |
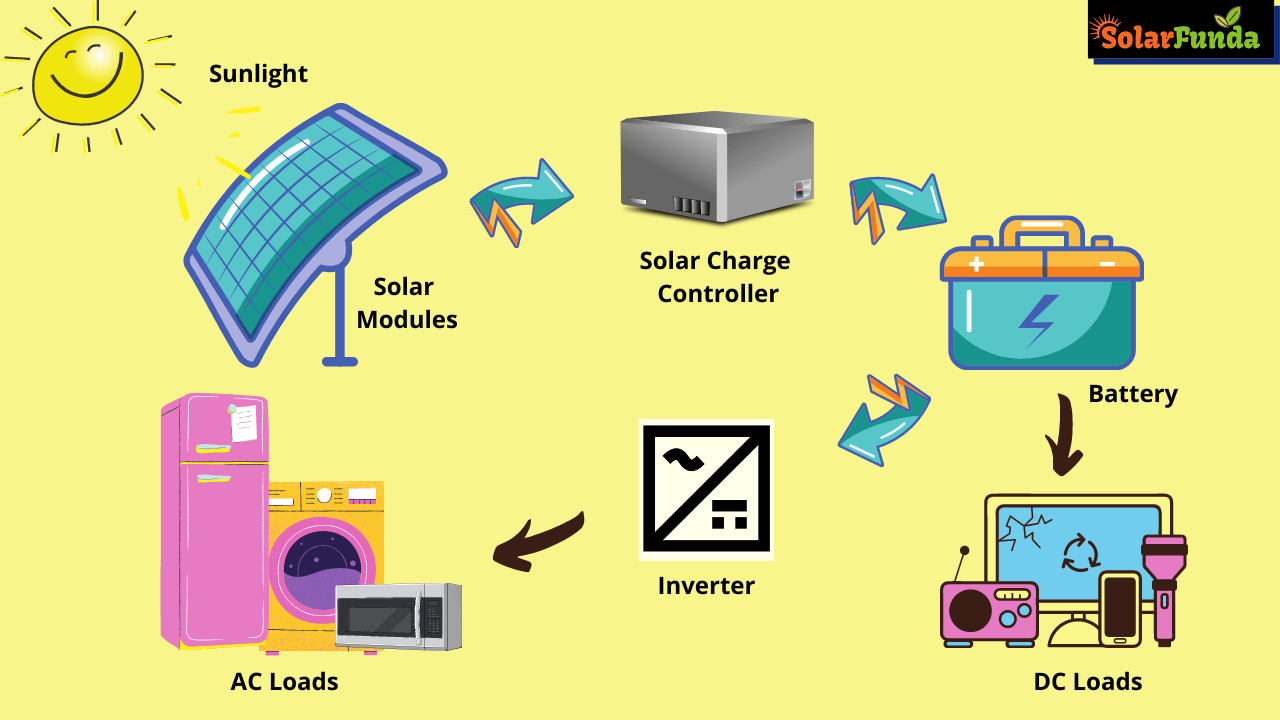
Solar Generator Technology

Harnessing the sun’s energy for off-grid living requires a sophisticated system. A solar generator isn’t simply a single device; it’s an integrated network of components working in concert to provide reliable power. Understanding these components is crucial for designing and maintaining an effective off-grid power solution.Solar generators consist of several key components that work together to convert sunlight into usable electricity and store it for later use.
The efficient interplay of these parts determines the overall performance and reliability of the system.
Solar Panel Types and Efficiency
Solar panels are the heart of any solar generator system, converting sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. Three main types of solar panels exist: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Monocrystalline panels boast the highest efficiency, typically ranging from 18% to 22%, due to their pure silicon construction. This translates to more power generation from a smaller surface area. However, they are also generally the most expensive.
Polycrystalline panels, made from multiple silicon crystals, offer slightly lower efficiency (around 15% to 17%) at a lower cost. Thin-film panels, the least efficient (around 8% to 13%), are known for their flexibility and lightweight nature, making them suitable for specific applications. The choice depends on budget, space constraints, and desired power output. For example, a homeowner with limited roof space might prioritize the higher efficiency of monocrystalline panels despite the higher initial cost, while a camper might opt for the lightweight nature of thin-film panels.
Battery Capacity and Types
The battery bank is the storage component of the solar generator, holding the DC electricity generated by the solar panels for use when the sun isn’t shining. Battery capacity, measured in amp-hours (Ah), determines how much energy the system can store. Larger capacity batteries are needed for longer periods of darkness or higher energy consumption. Two primary battery types are prevalent in off-grid systems: lead-acid and lithium-ion.
Lead-acid batteries are more affordable but have shorter lifespans and lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries, while more expensive upfront, offer significantly longer lifespans, higher energy density, and better efficiency, making them a popular choice for off-grid applications requiring reliable, long-term performance. For instance, a household with high energy demands might choose lithium-ion batteries for their longevity and superior performance, even if the initial investment is higher.
Inverters and Charge Controllers
The inverter converts the DC electricity from the solar panels and batteries into alternating current (AC) electricity, the type used by most household appliances. The choice of inverter depends on the power requirements of the appliances and the type of battery being used. A charge controller regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging and extending the lifespan of the batteries.
It’s a crucial safety component that protects the battery bank from damage. A poorly sized or malfunctioning charge controller can lead to premature battery failure, highlighting the importance of selecting an appropriate model for the specific solar panel and battery combination.
Sizing a Solar Generator System
Sizing a solar generator system requires careful consideration of energy consumption. A step-by-step approach ensures a properly sized system.
- Calculate daily energy consumption: List all appliances and their power consumption (in watts). Multiply each appliance’s wattage by its daily usage hours to determine its daily energy consumption (watt-hours). Sum the daily energy consumption of all appliances to find the total daily energy requirement (in watt-hours).
- Determine battery capacity: To account for cloudy days, aim for a battery capacity that can meet at least two days’ worth of energy consumption. Multiply the total daily energy requirement by two to determine the minimum battery capacity (in watt-hours).
- Calculate solar panel wattage: Consider the average daily sunlight hours in your location. Divide the total daily energy requirement by the average daily sunlight hours to determine the required solar panel wattage (in watts).
- Select components: Choose solar panels, batteries, an inverter, and a charge controller that meet the calculated requirements. Ensure that the inverter’s capacity is sufficient to handle the peak power demand of your appliances and that the charge controller is compatible with the chosen solar panels and batteries.
- Professional Installation: For safety and optimal performance, professional installation is highly recommended, especially for larger or more complex systems.
For example: A household uses 500 watt-hours of electricity daily. They should aim for a minimum battery capacity of 1000 watt-hours (500 Wh/day2 days). If they receive an average of 5 hours of sunlight daily, they need solar panels with a total wattage of 100 watts (500 Wh/day / 5 hours/day).
Embracing off-grid living with a solar generator system presents a unique opportunity to live sustainably and independently. While challenges exist in terms of initial investment and system maintenance, the long-term benefits – environmental responsibility, energy independence, and a simpler lifestyle – make it an increasingly attractive option for many. Careful planning, informed decision-making, and a commitment to energy conservation are key to successfully navigating this exciting and rewarding path.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of off grid living michigan.